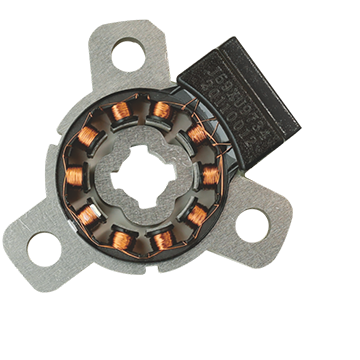
In the world of motion control and position sensing, variable reluctance resolvers play a critical role. These sensors are widely used in industrial automation, aerospace, robotics, and automotive applications due to their reliability, precision, and ability to function in harsh environments. The VR resolver is known for its ability to provide accurate position feedback in electromechanical systems.
This article will provide an in-depth exploration of the variable reluctance resolver, its working principles, applications, and benefits. We will also compare it with other types of resolvers and encoders to understand its advantages in various industries.
What is a Variable Reluctance?
Before diving into the specifics of a variable reluctance resolver, it is essential to understand the concept of variable reluctance itself.
Definition of Reluctance
Reluctance, in electrical engineering, is the opposition to the flow of magnetic flux in a magnetic circuit. It is analogous to electrical resistance in an electrical circuit. The formula for reluctance (R) is:
R=l/μA
Where:
l is the length of the magnetic path,
μ is the permeability of the material,
A is the cross-sectional area of the path.
Variable Reluctance Concept
In a variable reluctance system, the reluctance of the magnetic circuit changes dynamically based on the position of a moving component (typically a rotor). This change in reluctance is used to generate signals that provide information about position or speed.
What is a Variable Reluctance Resolver?
A variable reluctance resolver (VR resolver) is an electromechanical sensor that converts angular position into electrical signals. It operates based on the principle of variable magnetic reluctance, where the alignment of a rotor and stator modulates magnetic flux, inducing voltage signals that can be processed to determine angular position.
Key Components of a VR Resolver
A VR resolver consists of the following main components:
Stator: Contains multiple windings arranged in a specific pattern.
Rotor: A toothed structure that alters the magnetic reluctance as it rotates.
Excitation Coil: Provides the alternating current (AC) excitation signal.
Output Windings: Capture the induced voltage signals, which vary depending on the rotor position.
Comparison with Other Resolvers
| Feature | Variable Reluctance Resolver | Brushless Resolver | Optical Encoder |
| Operating Principle | Magnetic reluctance changes | Transformer coupling | Light interruption |
| Durability | High (no brushes) | High | Lower (sensitive to dust) |
| Accuracy | Moderate to High | High | Very High |
| Environmental Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher | Varies |
How Does a Variable Reluctance Resolver Work?
A variable reluctance resolver operates by detecting changes in magnetic reluctance as the rotor moves. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of its working principle:
1. Excitation Signal Generation
An alternating current (AC) excitation signal is applied to the primary winding of the stator. This AC signal generates a fluctuating magnetic field in the system.
2. Magnetic Flux Variation
As the rotor turns, its toothed structure alters the magnetic flux path. When the rotor teeth align with the stator poles, reluctance is minimized, leading to stronger magnetic coupling. Conversely, when misaligned, reluctance increases, weakening the coupling.
3. Induced Voltage in Secondary Windings
The varying magnetic flux induces voltage in the secondary output windings. The amplitude of these signals depends on the rotor position. By analyzing these signals, the angular position of the rotor can be determined with high accuracy.
4. Signal Processing
The induced voltage waveforms are processed using demodulation circuits or digital signal processors to extract position information. The output is typically in the form of sine and cosine signals, enabling precise angular calculations.
Mathematical Representation
The output voltages Vs and Vc can be expressed as:
Vs=Vmsin(θ)
Vc=Vmcos(θ)
Where:
By computing the ratio of these signals, the exact angular position can be determined using the inverse tangent function:
θ=tan−1(Vs/Vc)
Applications of Variable Reluctance Resolver
The VR resolver is widely used in various high-precision applications due to its robustness and reliability. Some of the major applications include:
1. Aerospace and Defense
Used in aircraft control systems for precise positioning of control surfaces.
Integrated into missile guidance systems for accurate trajectory control.
Employed in military-grade navigation systems.
2. Industrial Automation
Used in robotic arms for precise motion control.
Integrated into CNC machines for accurate tool positioning.
Applied in conveyor belt systems for speed and position feedback.
3. Automotive Industry
Essential for electric power steering (EPS) systems.
Used in hybrid and electric vehicles for motor position sensing.
Integrated into anti-lock braking systems (ABS) for wheel speed detection.
4. Renewable Energy
5. Medical Equipment
Advantages of VR Resolver Over Other Sensors
| Feature | VR Resolver | Optical Encoder | Hall Effect Sensor |
| Durability | High | Low | Moderate |
| Temperature Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Moderate |
| Electromagnetic Interference Resistance | High | Low | Moderate |
| Accuracy | High | Very High | Low |
Conclusion
The variable reluctance resolver is a crucial component in modern motion control and position sensing applications. Its ability to operate in extreme environments, resist electromagnetic interference, and provide accurate position feedback makes it an ideal choice for industries like aerospace, automotive, and industrial automation.
Compared to optical encoders and other position sensors, VR resolvers offer superior durability and reliability, making them indispensable in critical applications. As technology advances, we can expect further improvements in resolver design, enhancing their performance and expanding their use in emerging industries such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
FAQs
1. What is the main advantage of a variable reluctance resolver?
The main advantage of a variable reluctance resolver is its durability and reliability in harsh environments. Unlike optical encoders, it is resistant to dust, temperature variations, and electromagnetic interference.
2. How does a VR resolver compare to an optical encoder?
A VR resolver is more robust and can operate in extreme conditions, while an optical encoder provides higher resolution and accuracy but is more sensitive to environmental factors.
3. Can VR resolvers be used in electric vehicles?
Yes, VR resolvers are commonly used in electric vehicles for motor position sensing, ensuring efficient and precise control of electric powertrains.
4. What are the limitations of a VR resolver?
While VR resolvers offer excellent durability, they may have lower resolution compared to high-end optical encoders and require additional signal processing for accurate position detection.
5. How is a VR resolver different from an inductive resolver?
A VR resolver operates based on changes in magnetic reluctance, while an inductive resolver relies on transformer coupling between windings. Inductive resolvers generally offer higher accuracy but at a higher cost.









